English ![]()

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-05-08 Origin: Site
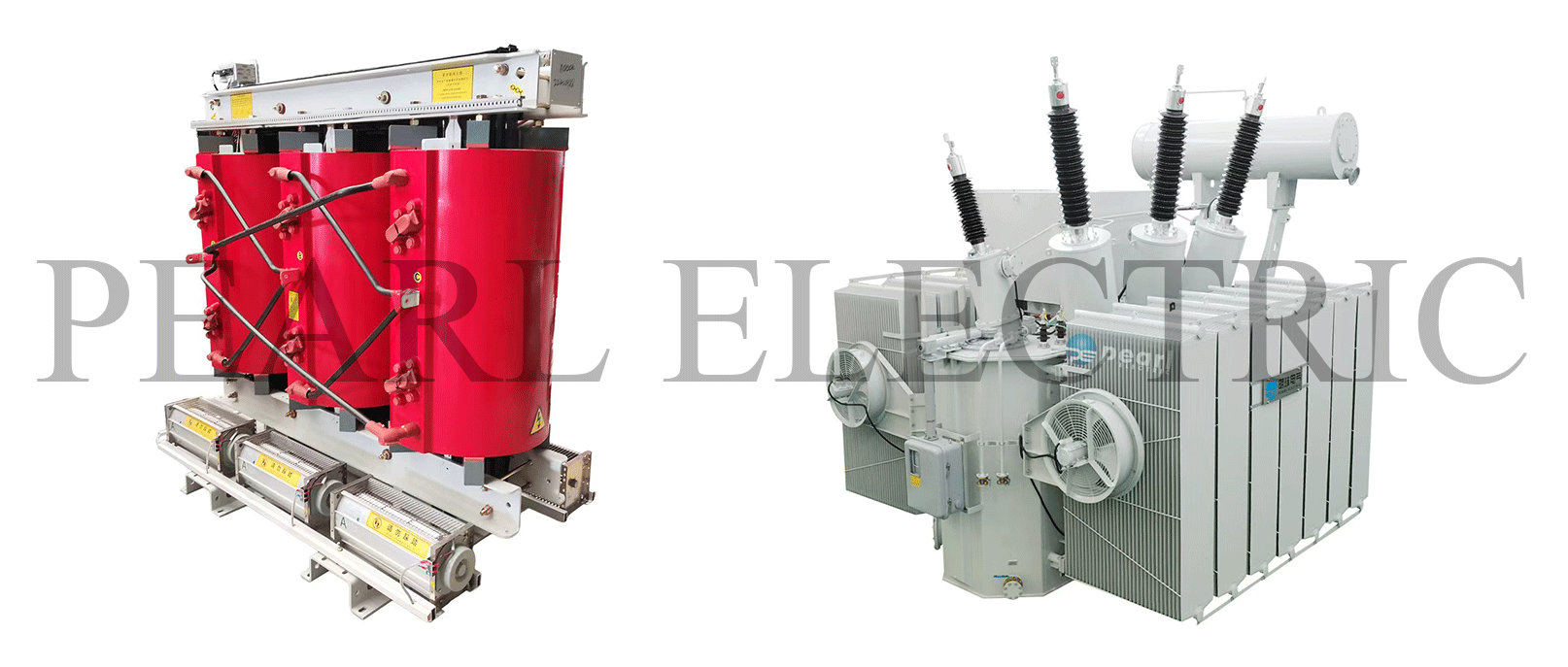
As critical components of power systems, the choice between dry-type and oil-immersed transformers significantly impacts power supply safety and cost efficiency. This guide analyzes their structural, performance, and application differences to help you make informed decisions.
Dry-Type Transformers:
Insulation: Epoxy resin casting or non-encapsulated solid insulation (e.g., Nomex paper).
Structure: Visible core/windings with silicone rubber bushings.
Oil-Immersed Transformers:
Insulation: Mineral or synthetic ester oil; fully submerged in a tank.
Structure: Sealed tank with porcelain bushings.
Type | Typical Capacity | Max Voltage | Key Applications |
Dry-Type | ≤2500kVA | 35kV (rarely 66kV) | Commercial buildings, Data centers |
Oil-Immersed | No limit (up to 1000kV) | Full voltage levels | Power plants, UHV transmission |
Cooling Efficiency:
Dry-Type: Natural/forced air cooling (limited efficiency).
Oil-Immersed: Oil circulation (superior for sustained high loads).
Overload Tolerance:
Dry-Type: ≤1.5x rated capacity (short-term).
Oil-Immersed: 30% overload for 1 hour.
Metric | Dry-Type | Oil-Immersed |
Initial Cost | 1.5x higher | Lower |
Maintenance | Low (no oil monitoring) | High (oil replacement, leak prevention) |
Lifespan | 20-30 years | 30-40 years (sealed design) |
Fire Safety: Hospitals, subways, skyscrapers (flame-retardant epoxy).
Space Constraints: Basements, compact substations (20% smaller size).
Eco-Sensitive Zones: Oil-free design compliant with RoHS.
High Power Needs: Thermal plants, industrial parks (≥10MVA).
Humid Environments: Coastal areas, mines (oil resists moisture).
Extreme Climates: Stable performance at -40°C to 45°C.

Define Requirements: Load type (continuous/shock/harmonic), environment (humidity/space).
Calculate Capacity: S = Load Power (kW) / Power Factor.
Match Features:
Fire safety → Dry-Type (SCB series)
High capacity/voltage → Oil-Immersed (S13-M series)
Cost-Benefit: Long-term → Dry-Type (low TCO); short-term → Oil-Immersed (low CAPEX).
Dry-Type:
Smart Monitoring: IoT-enabled sensors (e.g., Siemens CoolBlue).
High Voltage: Experimental 66kV models for offshore wind farms.
Oil-Immersed:
Eco-Upgrades: β-oil (fire point ≥300°C) replacing mineral oil.
Compact Design: Sealed corrugated tanks (15% smaller footprint).
Conclusion
Dry-type and oil-immersed transformers coexist as complementary solutions. With tightening regulations (e.g., EU Tier 3), dry-types dominate commercial sectors, while oil-immersed remain vital for energy infrastructure. For optimal selection, balance technical specs with lifecycle costs, and consult experts for tailored solutions.